Computer Science IT and AI
The journey of Computer Science, Information Technology (IT), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a fascinating one, full of breakthroughs that have transformed the way we live, work, and think.
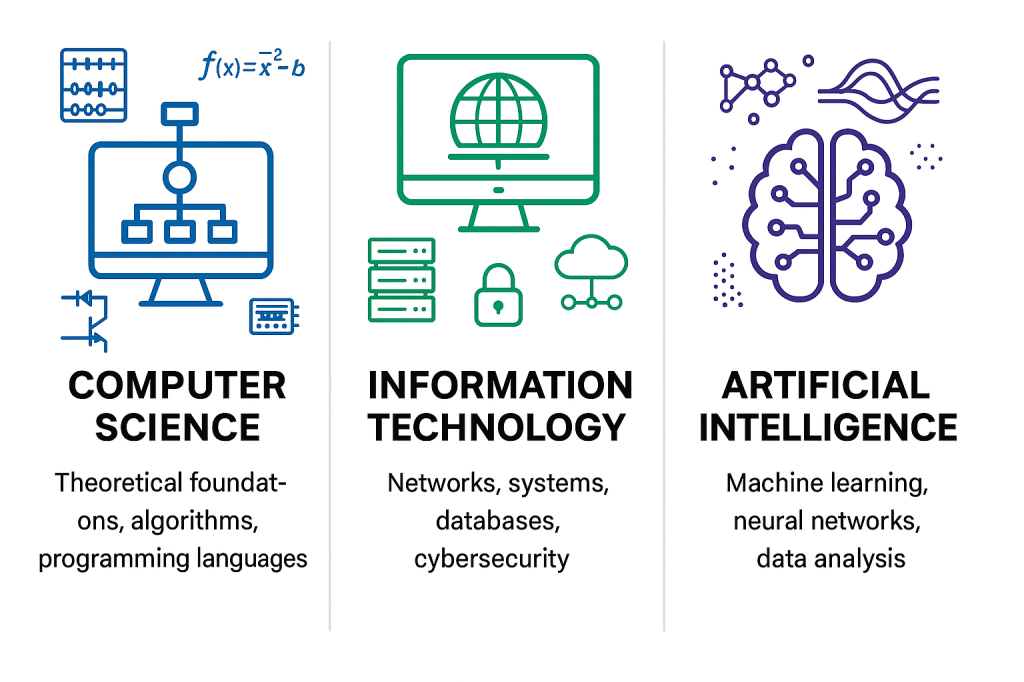
Computer Science: From Calculation to Computation
The roots of Computer Science date back centuries. Early computing devices, like the abacus and mechanical calculators, helped with basic arithmetic. But it was the 19th century genius Charles Babbage who designed the Analytical Engine, often considered the first conceptual model for a general-purpose computer. Then came Alan Turing, whose work in the 1930s laid the theoretical foundation for computing and algorithms.
The 1940s and 1950s saw the creation of the first electronic computers, like the ENIAC and the UNIVAC, which paved the way for modern computing. By the 1960s and 1970s, programming languages like FORTRAN, COBOL, and C emerged, establishing the field of software engineering.
Information Technology: The Digital Revolution
IT as a formal discipline emerged with the development of computers and networks. The invention of the internet in the late 20th century, thanks to ARPANET and TCP/IP protocols, set the stage for global connectivity. By the 1990s and 2000s, the rise of personal computers, websites, and the dot-com boom brought IT into everyday life.
Today, IT powers cloud computing, cybersecurity, and databases, ensuring seamless communication, automation, and digital transformation across industries.
Artificial Intelligence: From Dreams to Reality
The idea of AI—machines that mimic human thinking—can be traced back to ancient myths of automatons. However, AI as a formal field began in 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference, where pioneers like John McCarthy and Marvin Minsky explored the potential of intelligent machines.
Initially, AI focused on rule-based systems and problem-solving, but machine learning and neural networks revolutionized the field in the 1990s and 2000s. With the rise of deep learning, natural language processing, and generative AI, AI systems today can understand language, generate art, and even assist with complex decision-making.
From Babbage’s Engine to modern AI models, the history of Computer Science, IT, and AI is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of innovation.
Who are the key figures in Computer Science history?
Get a look at all of the famous contributors.
Main contributors
- Charles Babbage Known as the “father of the computer,” Babbage conceptualized the first mechanical computer, the Analytical Engine, in the 19th century. His design, though never fully constructed in his lifetime, introduced many ideas fundamental to modern computing, such as programmability and the use of punched cards for instructions.
- Ada Lovelace Working closely with Babbage, Ada Lovelace is often celebrated as the world’s first computer programmer. She saw beyond the machinery’s mechanical operations, envisioning a future where computers could manipulate symbols and create music or art—ideas that have resonated through every subsequent innovation in programming.
- Alan Turing A key figure in both theoretical and practical realms of computer science, Turing introduced the concept of the Turing Machine—a model for what it means to compute. His work during World War II on cryptographic machines, notably at Bletchley Park, not only contributed to the Allied victory but also established the theoretical framework for artificial intelligence and algorithm design.
- John von Neumann Von Neumann’s architectural model, commonly known as the von Neumann architecture, underpins virtually all modern computers. His vision of a stored-program computer, where both data and instructions reside in memory, is a cornerstone of how computers are built today.
- Grace Hopper Often referred to as “Amazing Grace,” Hopper pioneered the development of computer programming languages. She created the first compiler, which translates human-readable instructions into machine code, and played a critical role in developing COBOL, a language that made software more accessible across different computing systems.
- Claude Shannon A mathematician and electrical engineer, Shannon is hailed as the father of information theory. His groundbreaking work on quantifying information and digital circuit design not only transformed telecommunication but also provided the mathematical underpinning for modern data compression and error-correction techniques.
- Donald Knuth Knuth’s rigorous approach to algorithms and his seminal work, The Art of Computer Programming, have made him a central figure in computer science education and research. His analyses helped formalize the study of algorithms, influencing everything from software development to systems optimization.
- Edsger Dijkstra Known for his algorithmic innovations, like Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm, he was a formidable advocate for structured programming. His contributions reshaped how developers approach problem-solving and have had lasting impacts on both theoretical computer science and software engineering.
These individuals, among many others, have crafted the narrative of computer science—from abstract theories that define computation to concrete innovations that power our digital world. Their relentless curiosity and groundbreaking ideas continue to inspire new generations of technologists.
Timothy John Berners Lee

TimBL at some Data Center
What he contributed?
Timothy John Berners-Lee, widely known as Tim Berners-Lee, is a seminal figure in computer science whose contributions have fundamentally reshaped the digital landscape. Here are the key roles he played:
- Inventor of the World Wide Web While working at CERN in 1989, Berners-Lee proposed a system for managing and sharing information using hypertext. This idea materialized into the World Wide Web, a breakthrough innovation that turned the internet from a tool primarily for researchers into a universally accessible platform for information exchange. His initiative led to the development of the very first web browser and server, which allowed documents to be linked together via hypertext.
- Creator of Essential Web Protocols and Standards Berners-Lee didn’t just invent the medium; he also crafted the fundamental language and protocols that make the web function seamlessly. He developed HTML (HyperText Markup Language) for creating web pages, HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) for client-server communication, and the URL system, which standardized how web addresses are formatted. These protocols remain the backbone of the modern internet, ensuring that disparate systems can communicate effectively and that information remains universally accessible.
- Champion of an Open and Universal Web Understanding the potential of an interconnected world, Berners-Lee has been a staunch advocate for an open, decentralized web. He founded the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), an international community that develops open standards to ensure long-term growth for the web. His work with the W3C has helped promote interoperability and accessibility, ensuring that the web remains a public resource free from undue restrictions.
- Global Impact and Continuing Influence Beyond his technical innovations, Berners-Lee’s vision has impacted how societies interact, access information, and engage in commerce. His commitment to maintaining the web as an open platform has influenced policy debates around digital rights, privacy, and net neutrality. His legacy continues to shape discussions on technology governance and access, ensuring that the web remains a tool for empowering individuals globally.
Berners-Lee’s role in creating the World Wide Web is not just a milestone in computer science history—it’s a cornerstone of modern information society, impacting communication, education, and commerce around the world.
The About’s Words
-
Dramatized Lectures Vs Actual Science Lectures
I Found WHERE 3I/ATLAS Came From And What is Waiting There SHOCKED NASA – Avi Loeb Nov 10, 2025 #3iatlas #aviloeb NASA does not want you to know about. 3I/ATLAS…

